Skilled Trades Boom: Where Welding Jobs Will Surge by 2030
Welding is entering a growth cycle not seen in decades. Between new semiconductor fabs, EV and battery plants, LNG and petrochemical expansions, next‑gen nuclear, and offshore wind, the demand for certified welders and welding entrepreneurs is set to spike through 2030. This guide maps the hot sectors, pay trends, regional opportunities, the certifications employers are screening for, and a practical 6‑month upskilling roadmap aligned to common code requirements.
Why Welding Demand Is Set to Surge
- Reshoring and industrial policy: Fabs, batteries, and grid-scale energy projects are accelerating under federal and state incentives.
- Energy transition: LNG export terminals, hydrogen pilots, nuclear life‑extensions and SMRs, and offshore wind foundations all need high-skill welders.
- Aging workforce: Retirements outpace new entrants, especially in pipe welding and heavy fabrication.
- Automation expanding the pie: Robotic welding, orbital TIG, and laser processes still require certified operators, programmers, inspectors, and supervisors.
Sector-by-Sector Outlook
Semiconductor Fabs: Ultra‑High‑Purity (UHP) and Tool Install
Chip plants run on miles of stainless UHP tube and clean utility piping. Expect heavy demand for orbital GTAW (TIG), cleanroom discipline, and obsessive QA/QC.
- Key processes: Orbital GTAW on 316L/304L stainless tube (1/4–6 in), autogenous welds, cold‑wire GTAW, purge management, helium leak testing.
- Codes and standards: ASME Section IX welder qualification; ASME B31.3 Process Piping (High Purity service categories); owner specs; SEMI cleanliness protocols.
- Typical employer tests: Coupon-based orbital TIG bead geometry, autogenous tube welds with borescope inspection; GTAW manual stainless 6G on small‑bore; visual acuity and cleanliness audits.
- Hot spots: Arizona, Ohio, Texas, New York; secondary opportunities in Oregon and New Mexico.
- Pay snapshot: UHP tube welders/fitters commonly $32–$50/hr plus per diem; QA/borescope techs $28–$40/hr; supervisors higher.
EV and Battery Plants: High‑Volume and Advanced Materials
EV manufacturing blends high-throughput robotic GMAW with advanced aluminum and mixed‑material joining.
- Key processes: Pulsed MIG on aluminum (5xxx/6xxx), robotic GMAW, resistance spot welding (RSW), laser‑hybrid, fixture‑based production welding.
- Codes: AWS D1.2 (aluminum), AWS D1.1 (structural steel for building and mezzanines), OEM specs for production joints.
- Typical employer tests: Aluminum plate/tube pulsed‑MIG fillets and spray transfers; 3G/4G carbon steel GMAW or FCAW; robotic programming assessments.
- Hot spots: Tennessee, Georgia, Kentucky, North Carolina, Michigan, Texas.
- Pay snapshot: Production welders $22–$35/hr; robot techs/programmers $28–$45/hr; leadership higher, with OT common.
LNG, Pipelines, and Petrochem: The High‑Skill Pipe Core
Export terminals, cryogenic tanks, gas processing, and pipelines are classic welding job creators with strong OT.
- Key processes: GTAW roots with SMAW/FCAW fill and cap; all‑SMAW 6010/7018; SAW/FCAW for heavy structural; 9% Ni cryogenic procedures (specialty).
- Codes: API 1104 (pipelines), ASME B31.3/B31.8 (process/pipe), ASME Section IX (qualification), AWS D1.1 (structural steel).
- Typical employer tests: 6G carbon steel pipe (2–6 in sch. 80) GTAW root + SMAW fill/cap; downhill 5P+ for transmission; 3G/4G FCAW on 1 in plate with bends or UT.
- Hot spots: Texas and Louisiana Gulf Coast; New Mexico and West Texas (Permian); Pennsylvania/Ohio/West Virginia (Appalachia).
- Pay snapshot: $35–$55/hr for combo pipe welders, often plus per diem; turnaround/shutdown OT drives total comp well into six figures.
Nuclear: Life‑Extensions and Advanced Reactors
Existing fleet maintenance and new advanced nuclear projects demand top‑tier welding, documentation, and quality culture.
- Key processes: Narrow‑groove GTAW/GMAW, dissimilar metal welds (Alloy 52/152), stainless and nickel alloys, strict heat‑input control.
- Codes and QA: ASME Section III and XI, ASME Section IX, NQA‑1 quality programs, owner/utility procedures.
- Typical employer screens: 6G GTAW/SMAW on carbon/stainless with RT/UT acceptance; background, drug/alcohol (FFD), respirator fit, color‑vision for PT/MT.
- Hot spots: Southeast (fleet upgrades), select Midwest and Mountain West for advanced reactor sites.
- Pay snapshot: $40–$60/hr plus premiums; supervisors/lead auditors higher.
Offshore Wind and Heavy Fabrication: Big Steel, Harsh Environments
Tower sections, transition pieces, jackets/monopiles, and port upgrades create sustained heavy‑fab demand.
- Key processes: FCAW‑G for out‑of‑position, SAW for long seams, GMAW, thermal cutting/gouging, preheat/interpass control on thick plate.
- Standards: AWS D1.1 (structural steel) and D1.5 (bridge) for comparable demands; project specs often reference DNV/ABS; ISO 3834 for fab quality.
- Typical employer tests: 3G/4G FCAW (flux‑cored) with bend tests; SAW procedure familiarity; VT competency and WPS compliance checks.
- Hot spots: New York/New Jersey, Rhode Island/Massachusetts, Virginia; Gulf Coast yards fabricating large components.
- Pay snapshot: $34–$50/hr, with differentials for offshore, night shifts, and union scale on some projects.
Certifications That Open Doors
- AWS D1.1 Structural Steel: 3G/4G FCAW/GMAW plate tests with guided bends; widely requested for fab/erection.
- API 1104 Pipe: 5G/6G SMAW or GTAW/SMAW combo on carbon steel; common on transmission/distribution lines.
- ASME Section IX Welder Performance Qualifications: GTAW/SMAW/GMAW on pipe and plate for B31.3/B31.8 work; stainless and nickel alloy endorsements boost value.
- AWS D1.2 Aluminum: Pulsed/spray GMAW on 5xxx/6xxx alloys for EV/battery and material‑handling equipment.
- Orbital GTAW Training/Qualification: Vendor or contractor qualifications for UHP tube with borescope acceptance; helium leak familiarity is a plus.
- Safety and site access: OSHA 10/30, Confined Space, Aerial Lift, Rigging, and TWIC for ports and petrochem sites.
- NDE exposure: VT Level I and PT Level I help you communicate defects, acceptance criteria, and pass first‑time.
Pay Trends and Work Arrangements
- Per diem leverage: Travel welders in LNG, fab yards, and shutdowns often earn $100–$165/day per diem plus $35–$55/hr and OT.
- Shift premiums: Nights and 6‑10s (six days, ten hours) significantly lift weekly checks.
- Union vs. open shop: Building trades offer training and benefits with scale pay; open shop can move faster with performance bonuses.
- Specialty premiums: UHP tube, cryogenic alloys, narrow‑groove GTAW, or orbital programming typically command higher rates.
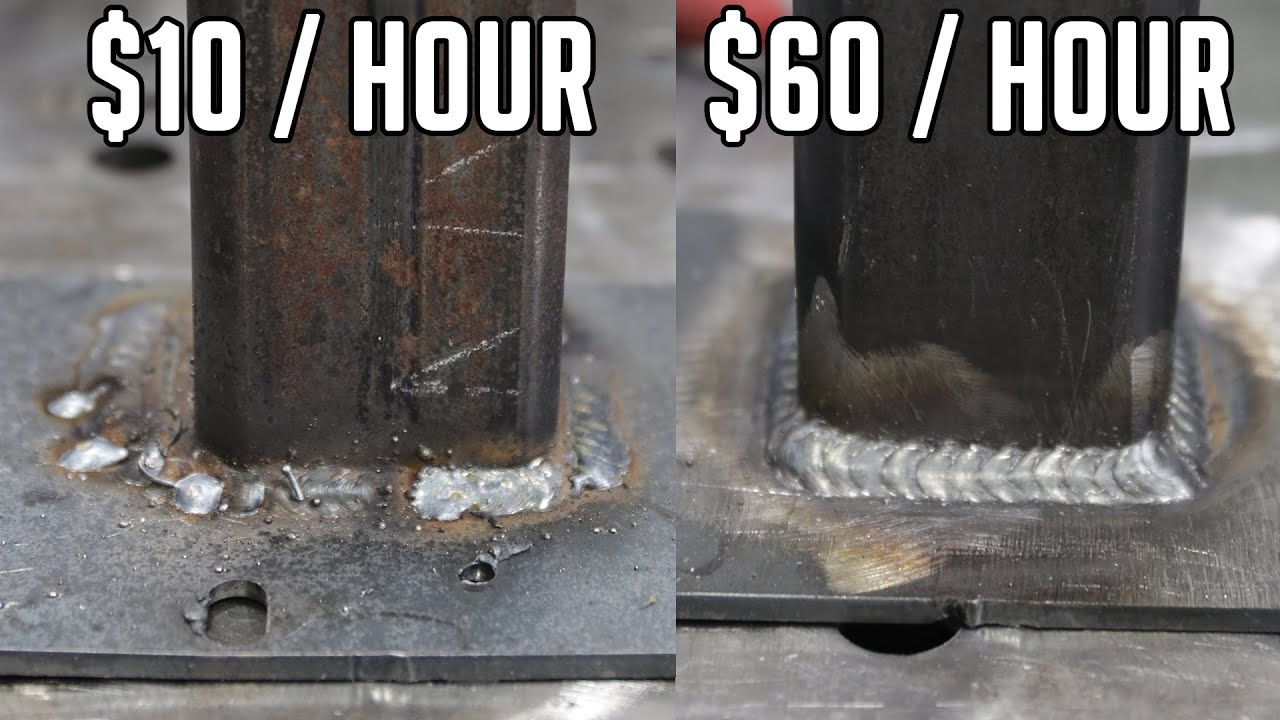
Remember: employers pay for productivity and reliability. Clean RT/UT, minimal repair rates, and WPS discipline are worth more than raw arc time.
Regional Hot Spots Through 2030
- Semiconductors: Phoenix/Tucson (AZ), Columbus (OH), Austin (TX), Upstate NY.
- EV/Batteries: Nashville/Chattanooga (TN), Atlanta/Savannah (GA), Bluegrass (KY), Charlotte/Greensboro (NC), Detroit (MI), Austin (TX).
- LNG/Petrochem: Houston/Beaumont/Port Arthur (TX), Lake Charles/Baton Rouge (LA), Corpus Christi (TX), Permian Basin (TX/NM), Appalachia (PA/OH/WV).
- Offshore Wind/Ports: New Bedford (MA), Providence (RI), New York/New Jersey ports, Hampton Roads (VA); heavy fab in Gulf Coast yards.
- Nuclear: Carolinas, Tennessee Valley, Georgia, select Midwest/Mountain West sites for advanced reactors and component manufacturing.
A 6‑Month Upskilling Roadmap (Aligned to Employer Tests)
Month 1–2: Foundation and Code Familiarity
- Processes: Daily SMAW (E6010/E7018) and GTAW (carbon/stainless) on plate and small‑bore coupons. Target stringer discipline and heat input control.
- Code literacy: Read WPSs and PQRs; learn essential variables (ASME IX), preheat, interpass, and acceptance criteria (AWS D1.1 visual and bend basics).
- QA habits: Weld maps, traceability, filler control, purge etiquette, cleanliness (especially for UHP).
Month 3: Structural Plate Proficiency
- Goal: Pass AWS D1.1 3G and 4G FCAW with guided bends.
- Practice: 3/8–1 in plate, FCAW‑G, multi‑pass with proper interpass temp; bevel prep, back‑gouging, and defect control (undercut, LOF, porosity).
- Validation: Conduct internal bend tests; if possible, third‑party test to carry a current card.
Month 4: Pipe—Your Ticket to Premium Work
- Goal: 6G carbon steel pipe, GTAW root/hot, SMAW fill/cap to ASME IX with RT/UT acceptance (B31.3/API 1104 style).
- Practice: 2–6 in sch. 80; feathered lands, tight gaps, gas lens, purge dams; switch to 7018 for fill and cap with consistent reinforcement.
- Mock employer screen: Timed test, WPS review, visual standards, and fit‑for‑duty checks.
Month 5: Stainless/UHP and Aluminum
- Stainless/UHP: Orbital GTAW head setup, autogenous welds on 1/2–1 in tube; borescope evaluation, coupon cleaning, and helium leak basics.
- Aluminum: Pulsed‑MIG on 5xxx/6xxx plate/tube; joint prep, wire feeding, distortion control; align with AWS D1.2 fillet/plate tests.
Month 6: Documentation, NDE, and Employability
- NDE literacy: VT and PT Level I coursework; practice discontinuity calls against code acceptance tables.
- Safety/site: Complete OSHA 10/30, Confined Space, Aerial Lift; secure TWIC if targeting ports/LNG.
- Test day rehearsal: Full 6G or 3G/4G under realistic time limits; organize a welder portfolio (WQTRs, photos, references, tool list).
Weekly cadence: 15–20 hours of arc time, 2–3 hours of code/NDE study, and one timed mock test. Track heat input, travel speed, and repair rates to show measurable improvement.
Gear and Tech to Watch
- Advanced waveforms: RMD/STT/CMT for root pass control, pulsed GMAW for aluminum and positional work.
- Orbital GTAW systems: Data‑logged welds, auto‑height control, and closed‑head UHP capability are in demand at fabs.
- Cobots/robots: Quick‑teach pendants, through‑arm MIG, and seam‑tracking cameras—the job is increasingly programmer‑operator hybrid.
- Laser and hybrid laser‑arc: Growing in EV/body structures and precision fab; strong fixturing and fit‑up are critical.
- Fume control and PPE: High‑efficiency extraction and PAPR helmets are becoming standard on big jobsites.
Quick Checklist to Get Hired Faster
- Current WQTRs for AWS D1.1 plate and a 6G pipe ticket (ASME IX/API 1104).
- Safety cards (OSHA 10/30) and TWIC; respirator fit test if available.
- Clean, organized welder portfolio: WPS/PQR familiarity, photos of test coupons and accepted welds, NDE training certificates.
- Tooling: Purge gear, gas lens kits, aluminum consumables, fillet gauges, hi‑lo gauge, borescope familiarity for UHP.
- Readiness: Willingness to travel, pass hair/urine drug tests and background checks, and work 6‑10s during peak.
Key Takeaways
- By 2030, welding jobs surge in semiconductors, EV/battery, LNG/petrochem, nuclear, and offshore wind—each with distinct processes and codes.
- Must‑have certs: AWS D1.1 plate, API 1104 or ASME IX 6G pipe, and aluminum or orbital TIG credentials for EV and fab work.
- Pay climbs with portability: Travel, per diem, clean NDE, and code literacy can push earnings into six figures.
- A focused 6‑month plan can align your skills to real employer screens and code requirements.
Conclusion
The next five years will reward welders who pair strong arc skills with code discipline and modern tools. Whether you want to chase per diem on LNG turnarounds, master orbital TIG for fabs, or program robots in EV plants, there’s a lane for you. Get the right certs, practice to the test, and bring a quality mindset—opportunity will meet you at the hood.