Weighing Portability, Power, and Certification Impacts
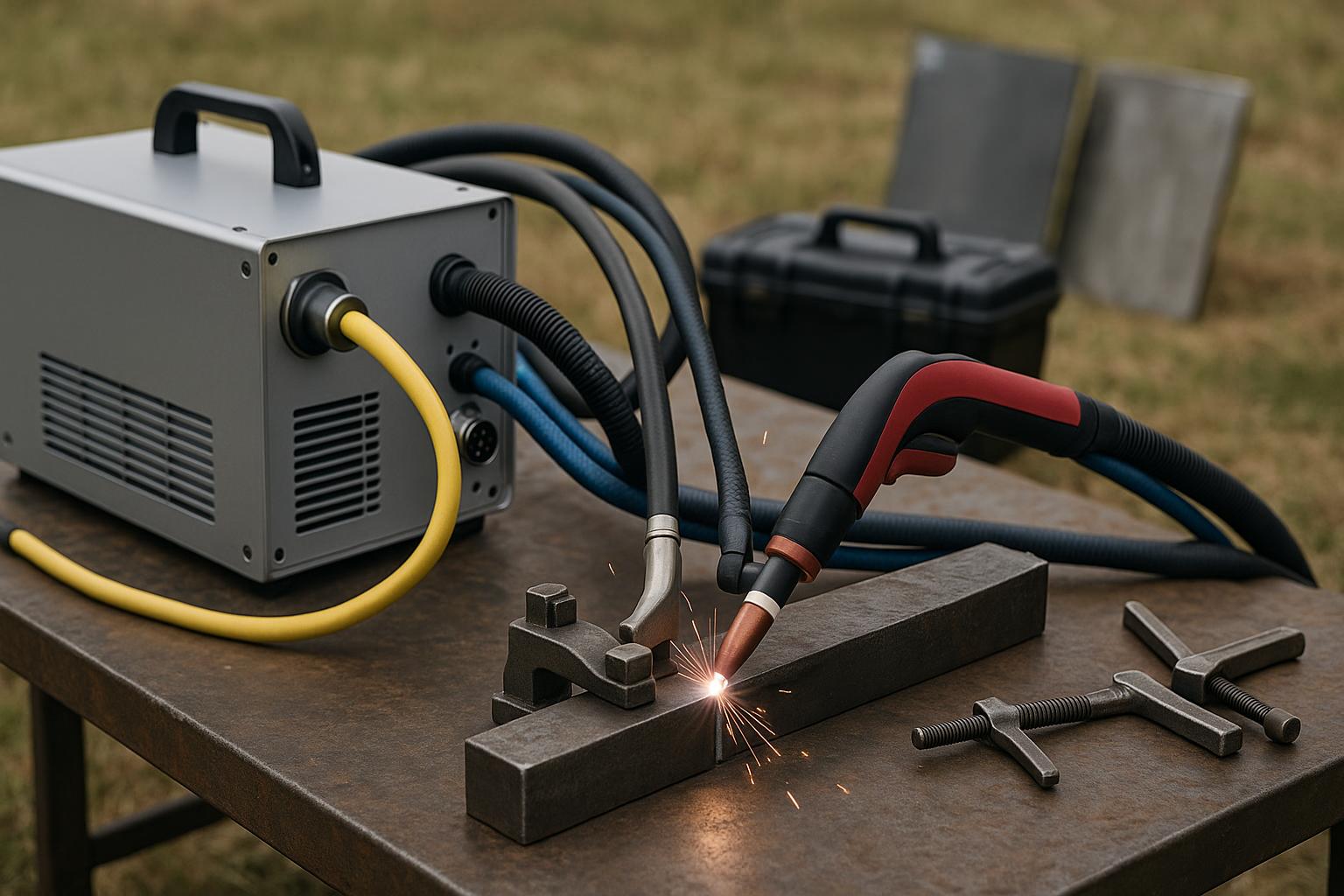
Laser-assisted TIG hybrids bring field-ready precision to portable welding. They merge a fiber laser with a TIG arc to allow deeper, cleaner welds with controlled heat input. For startups delivering in-the-field service, portability, setup time, and certification-readiness are the core tradeoffs.
Portability and setup: Look for compact power supplies, integrated cooling, and minimal alignment steps. A system with plug-and-play torch assemblies reduces field downtime. For portable field power considerations, see portable hybrid power.
Certification readiness: Labs expect documented procedures, WPS alignment, and traceable test records. Design field practice around lab-style blocks so the transition to certification testing is smooth. Techniques like arc monitoring can be part of your in-field process readiness: arc monitoring, and other smart power strategies are covered in related guides like dock-ready power resources.
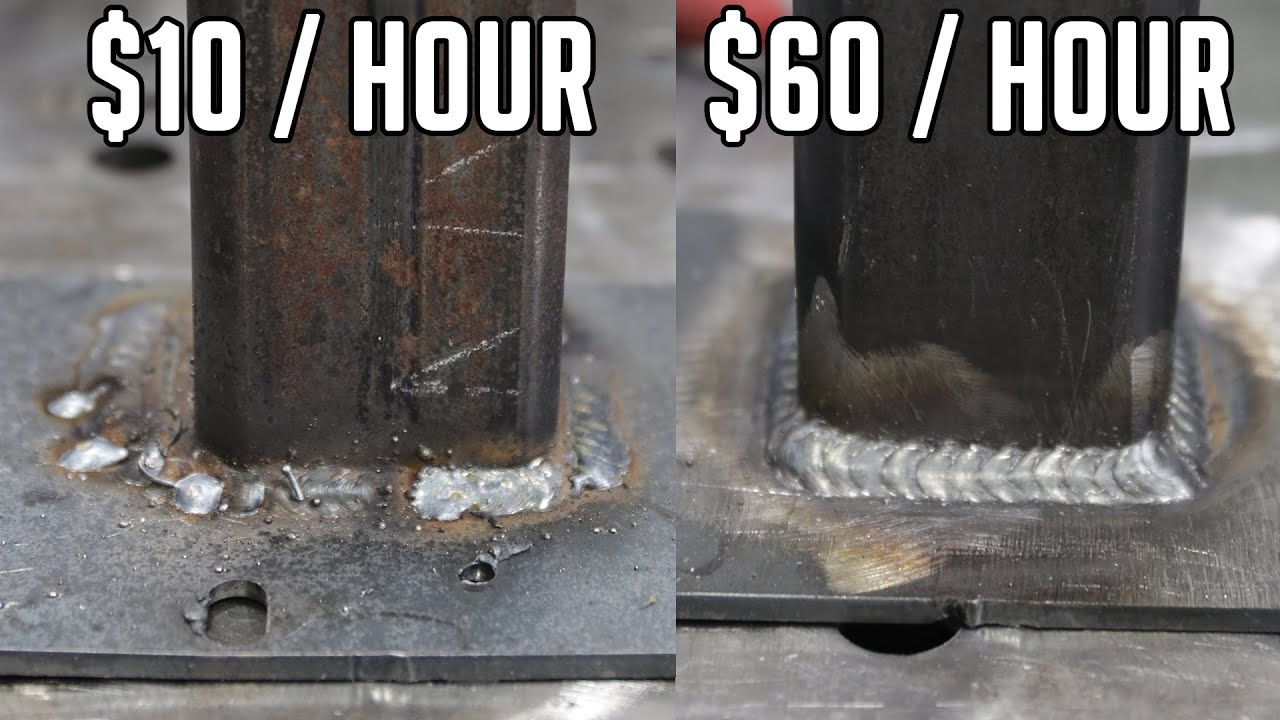
Run-length and process control: Laser-assisted TIG can increase productive weld time by reducing post-weld cleanup, but heat management remains critical on complex joints. Schedule mock-field trials that mimic lab fixtures, measure travel speed, and document bead quality using objective criteria similar to certification tests.
Practical setup patterns for field startups
- Define a minimal, certification-ready workcell that fits a trailer or pickup bed.
- Pre-wire WPSs and PQRs so a technician can qualify a bead within a standard lab window.
- Schedule practice sessions that mirror certification testing timing blocks.